Introduction
In today’s fast-paced work environment, efficiency is everything. If you’ve ever found yourself performing the same repetitive tasks in Microsoft Word—formatting documents, inserting boilerplate text, or running complex edits—there’s a powerful solution: macros.
Macros are small, automated scripts that execute a series of commands with a single click or keyboard shortcut. While they may sound technical, even non-programmers can use them to drastically cut down on manual work. As someone who has automated workflows for legal firms, content teams, and administrative staff, I’ve seen macros turn hours of tedious formatting into a one-second task.
In this guide, we’ll break down how macros work, why they’re a game-changer, and real-world examples of how businesses use them to boost productivity.
What Are Macros, and How Do They Work?
A macro is a recorded sequence of actions in Word that can be replayed later. Instead of manually performing steps like applying styles, inserting tables, or running find-and-replace operations, you can automate them.
Key Concepts:
Recording a Macro: Word tracks your actions (keystrokes, clicks, formatting) and saves them as a script.
Running a Macro: Once recorded, the macro can be executed with a button, shortcut, or menu command.
VBA (Visual Basic for Applications): Advanced users can edit macros in this programming language for more complex automation.
Example:
A receptionist at a medical office records a macro that:
A receptionist at a medical office records a macro that:
Inserts a patient intake form template.
Applies standardized formatting.
Adds today’s date automatically.
What used to take 5 minutes now happens instantly.
How to Record a Simple Macro (Step-by-Step)

You don’t need coding skills to start using macros. Here’s how to create one:
Steps to Record a Macro:
Go to View > Macros > Record Macro.
Name your macro (e.g., “FormatReport”) and assign a shortcut (like Ctrl+Shift+F).
Perform the actions you want to automate (e.g., apply Heading 1 style, set margins, insert a footer).
Click Stop Recording when done.
Now, pressing Ctrl+Shift+F will repeat those steps automatically.
Pro Tip:
Avoid unnecessary clicks while recording—macros replicate everything, including mistakes!
Real-World Uses of Macros in Business
Macros aren’t just for tech experts. Here’s how different industries use them:
Legal Firms:
Automatically apply court document formatting (font, spacing, page numbering).
Insert pre-approved clauses from a library.
Content Teams:
Convert Markdown to Word formatting with one click.
Batch-remove extra spaces and line breaks in edited drafts.
Administrative Staff:
Generate numbered meeting minutes templates.
Auto-fill repetitive fields in forms (e.g., invoice dates).
Case Study:
An HR department reduced onboarding time by 40% by using macros to generate offer letters—pulling names, job titles, and salaries from an Excel sheet into Word.
Advanced Automation: Editing Macros with VBA
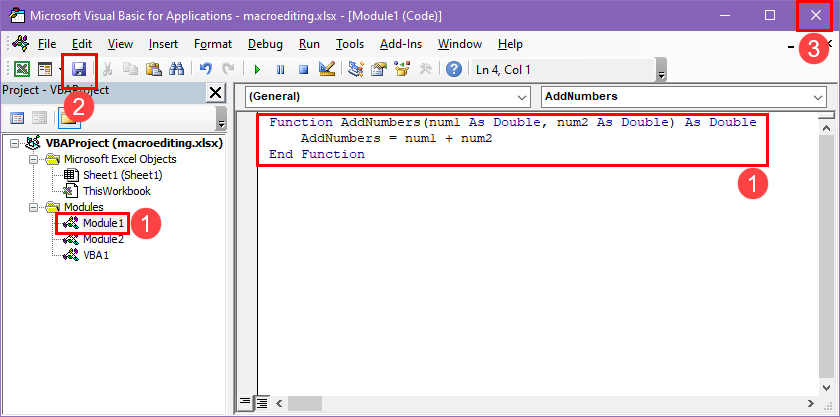
For power users, Word’s VBA editor (Alt + F11) unlocks even more automation.
What You Can Do with VBA:
Loop through documents to apply bulk changes.
Extract data from Word to Excel automatically.
Create custom dialog boxes for user input.
Example Script:
A simple VBA macro that saves time:
vba
Copy
Download
Sub InsertSignature()
Selection.TypeText “Best regards,” & vbCrLf & “John Doe”
End Sub
This inserts a pre-written signature with a single click.
Security Considerations: Are Macros Safe?
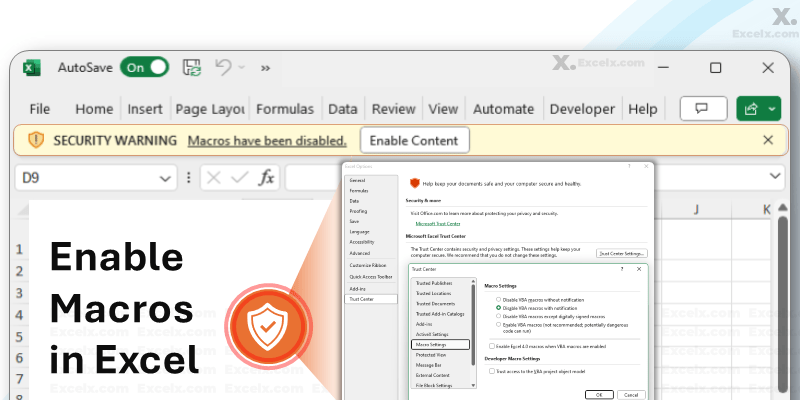
Macros can be powerful but also pose risks if misused:
Best Practices:
Only enable macros from trusted sources (avoid unknown .docm files).
Use Digital Signatures to verify macro authenticity.
Keep macros disabled by default (adjust in File > Options > Trust Center).
Note: Many organizations restrict macros due to malware risks, so check your company’s IT policies first.
Conclusion
Macros turn Microsoft Word from a basic word processor into a productivity powerhouse. Whether you’re recording simple formatting shortcuts or writing VBA scripts for complex tasks, automation can save hours—or even days—per year.
Start small: record a macro for one repetitive task this week. Once you see the time savings, you’ll wonder how you ever worked without them.
Ready to automate? Press Record and let Word do the work for you.